Glucometer used as diabetes check machine
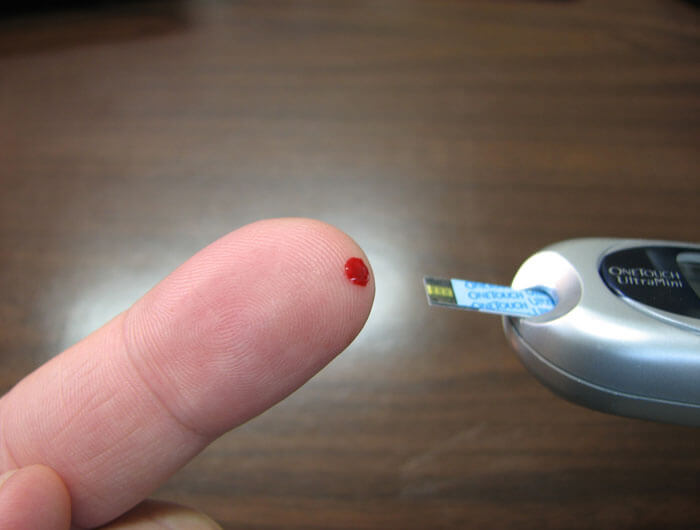
Individuals with diabetes know the importance of their blood sugar levels. A Diabetes check machine, i.e., glucometer, is a device that helps you do just that. But what is a glucometer, and how does it work? Read on to find out.
Diabetes mellitus is one lifestyle disorder that is quickly becoming a worldwide predicament. Type I and Type II are two types of diabetes in which blood and urine glucose levels can determine. Managing diabetes is hard. But with this tool, you can monitor your blood sugar levels as you go about your day.
What is a glucometer?
A Glucometer is a diabetes-management device used to measure the amount of glucose in your blood. It’s important for people with a high risk of diabetes and those fighting diabetes to use this device. A Glucometer is a key element of home blood glucose monitoring for people with diabetes and is universally used to help manage hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
Why do you need to keep a check on blood glucose levels?
A check on blood glucose levels is important for an individual with diabetes. Uncontrolled diabetes leads to eye and kidney complications. So, it is very important to keep a check on blood glucose levels regularly with a glucometer as.
- To manage blood sugar levels.
- To help manage insulin doses.
- To track diet and daily activities.
- To avoid the risk of sudden changes in glucose levels.
- To reduce the risk of diabetes complications.
Suggested Read: World Diabetes Day
How to use a Diabetes check machine?
A glucometer, often known as a Diabetes check machine, is a device that measures blood glucose levels. It is a small instrument that measures the quantity of glucose in the blood using a small drop of blood. The device is simple to operate. Want to know how?
- It has a monitor and a lancet or fingerprick device and uses a blood test strip to show the blood glucose level in the blood.
- The meter reads and determines the blood glucose level by measuring a little drop of blood collected by pricking the skin with a lancet.
A person with diabetes is instructed to check their glucose level recurrently to monitor the changes. The blood glucose test has been categorised into different types like Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS), Random Blood Sugar (RBS), Parts Per Million (PPM) etc. (1)
| Result | Fasting Blood Sugar Test | Random Blood Sugar Test |
| Diabetes | 126 mg/dL or above | 200 mg/dL or above |
| Pre-Diabetes | 100 – 125 mg/dL | N/A |
| Normal | 99 mg/dL or below | N/A |
The Diabetes Center has guidelines for blood glucose readings. Insulin tolerance declines with age, increasing the risk of diabetes in an individual. This is called a target range. Sometimes your healthcare provider gives you a different target range, like bedtime, exercise, or after eating. The following table provides a blood sugar levels chart by age (1);
| Age | Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Fasting (FBS) |
| 0-5 years old 6-12 years old 13-19 years old 20+ years Age 20+ years Age | >80 to 180 mg/dL >80 to 180 mg/dL >70 to 150 mg/dL 20+ years Age 70 to 89 mg/dL |
The accuracy of the values is set to +/- 15% compared to lab values of blood sugar levels charted by age. However, calibration of the machine, proper placement of the drop, and temperature may all affect the values. If there is a drastic change in the blood glucose value, repeat the test 3 times before checking with a laboratory.
What are the different types of glucometers available?
Different types of glucometer or Diabetes check machines are there on the market. The market is vast, from the most advanced Illustration depicting glucometers with strips to regular glucometers.
A. Invasive glucometer:
- Size: The average size is approximately the size of a palm.
- Strips: Glucose oxidase strips are common; discs, drums, and cartridges are also useful.
- Coding: The coding is varied from batch to batch. One touch has its test strips around a specific code number.
- The blood volume: The drop size varies according to models.
- Alternate site testing: Pricking of forearms or other areas rather than fingertips.
- Testing time: It may vary from 3sec to 60sec.
- Display value: mg/dl or mmol/l
- Clock / Memory: Most glucometers store past findings also for accurate reference.
- Data transfer: The result can be downloaded by cable or IR to a computer and read by the software.
- Cost: The cost may start from 1000rs.
B. Non-invasive meters:
- Works by electrically drawing glucose through unbroken skin and is removed after a brief time. However, it is inaccurate and will display the interstitial fluid’s glucose level, which is lower than the blood glucose level.
How does glucometer detection work?
A glucose meter has two essential parts: an enzymatic reaction and a detector. The enzyme for the glucose meter is usually in a dried-out state and comes in a disposable strip or reaction cuvette. To test the patient’s blood sample, the enzymes and glucose are mixed to create a product that the machine can detect.
When is it needed to repeat a test?
Individuals with Type I diabetes may often test 4 to 10 times a day due to dynamics of insulin adjustment, whereas type II Diabetics typically test less frequently.
A glucometer is a helpful device for monitoring blood glucose levels chart by age. It is feasible and patient compliant. A person with diabetes should keep his blood sugar levels under control. If it is under control, it will be easier for the body to use insulin and convert food into energy.
Suggested Read: Diet Exercise and Weight loss
Reference:
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/diabetes-testing/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/getting-tested.html






